EXPLORE Golden Mountains of Altai with this slideshow, check the location map and get all the facts and information below.
For slideshow description see right or scroll down (mobile). Click to view slideshow
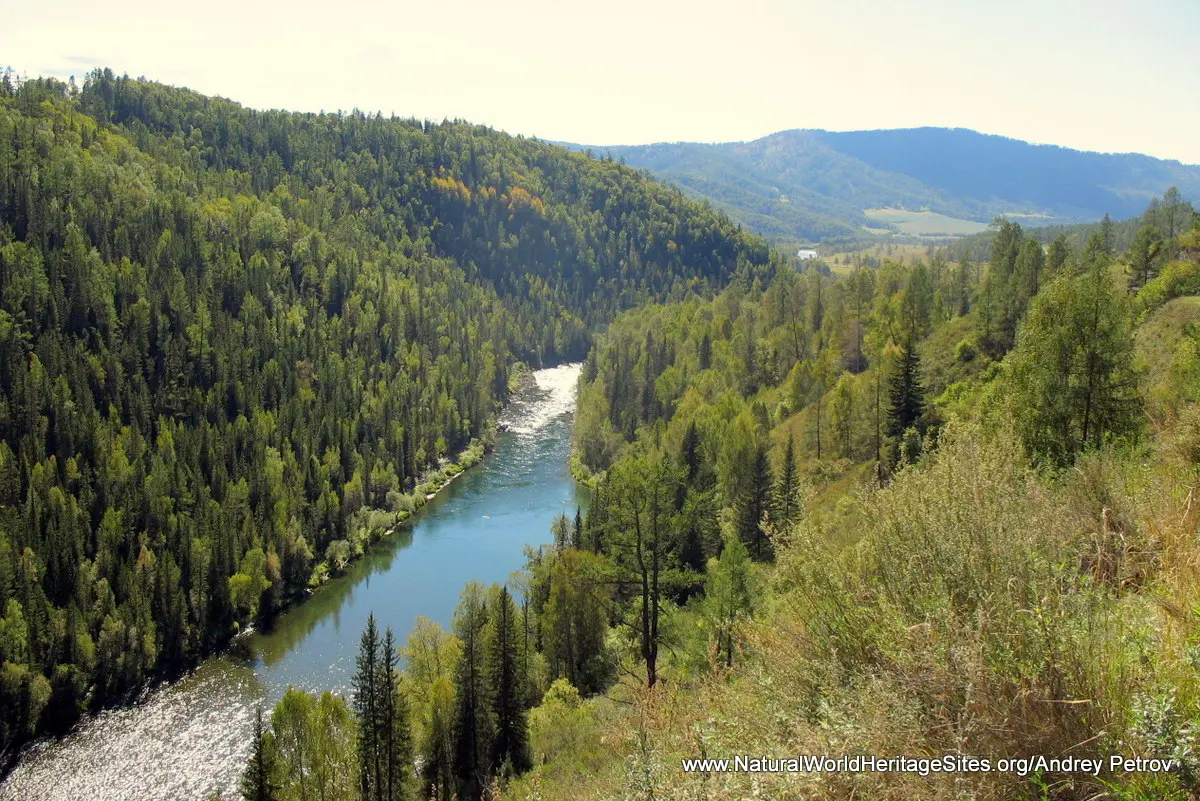
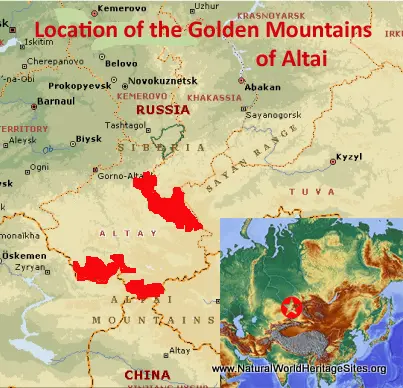
Location and Values: The Golden Mountains of Altai World Heritage Site is located in southern Siberia, close to Russia’s border with Kazakhstan, China and Mongolia. It includes three separate areas which protect a diverse assemblage of plant and animal species associated with different vegetation zones over a wide range of altitude from the relatively warm lowlands at 430m to the summit of Mount Belukha at 4,605m. The landscapes include forest-steppe; coniferous, open and mixed forest types; sub-alpine meadows; alpine tundra; rock and ice; a multitude of glacial lakes; and other glacial features. More than 10% of the area’s 2,000 species of vascular plants are endemic to the Altai region, and it’s 72 known species of mammals include rare species such as snow leopard, Altai argali (a wild sheep), and Siberian ibex. The area protects important water catchment zones, and includes Siberia’s second largest, most pristine and biologically diverse lake, Lake Teletskoe.
Conservation Status and Prospects. According to IUCN’s Conservation Outlook Assessment (2017) the conservation status of the Golden Mountains of Altai is ‘good, with some concerns’. The IUCN report notes that protection of the site benefits from its remote location, large size and the commitment of conservation and management authorities. There are no major threats, but local community use of a broad range of natural resources, for example medicinal plants, may exceed sustainable levels in some cases. Poaching is a threat to populations of several species of conservation concern including Argali sheep, Siberian ibex, musk deer and snow leopard. Livestock grazing is widespread, particularly in the Ukok Plateau area, where grazing intensity may exceed rangeland capacity. This results in a number of negative impacts including soil erosion; changes in the species composition of native vegetation; competition and displacement of native grazing animals; disease transmission between livestock and native fauna; and the elimination of predators, such as snow leopards and wolves, by livestock herders. Tourism is still very low and has little impact on the site, but requires some management attention locally. Potential long-term threats include the impacts of climate change and a long-standing proposal for construction of a gas pipeline through the Ukok Plateau area.
Links:
Google Earth
Official UNESCO Site Details
IUCN Conservation Outlook
UNEP-WCMC Site Description
Birdlife IBA
Slideshow description
The slideshow ‘tells the story’ of the Golden Mountains of Altai with a portfolio of photos by Andrey Petrov.
Factfile
Website Category: Mountains;
Temperate Grasslands, Steppes, Shrub-Lands & Tundra
Area: 16,115 km2
Inscribed: 1998
Criteria:
- Natural habitat for biodiversity (x);
- Significant number of rare, endemic and/or endangered species (x)