EXPLORE the Hubei Shennongjia with this slideshow, check the location map and get all the facts and information below.
For slideshow description see right or scroll down (mobile). Click to view slideshow
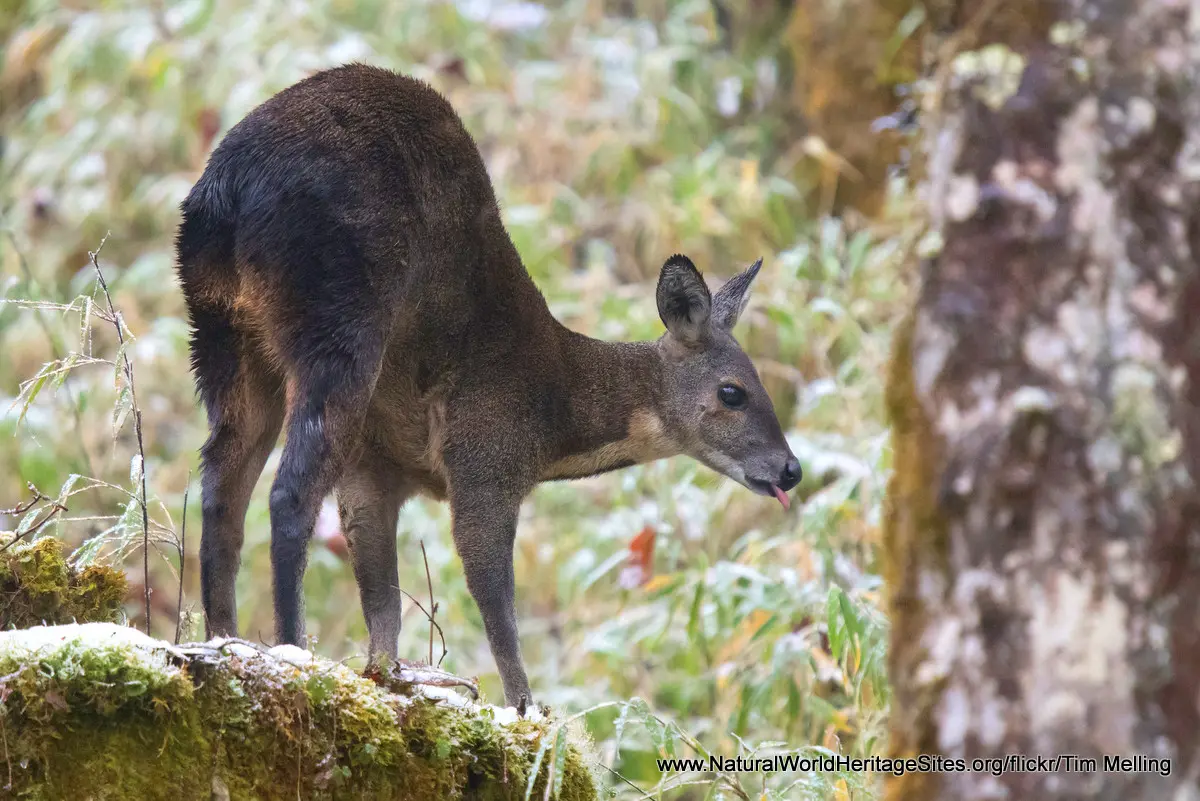
Location and Values: Hubei Shennongjia is located in a mountainous region of central China, where it protects the largest remaining primary forests covering the most complete altitudinal gradients of mixed evergreen and deciduous broad-leafed forests in the world. The site’s wide altitudinal range, from 420m to 3,106m above sea level, results in an extraordinarily diverse flora and fauna, with very high levels of species richness and endemism. There are 11 distinct vegetation types, from sub-tropical evergreen broad-leafed forests through various deciduous forest communities to temperate conifer and subalpine meadows at higher elevations. Records indicate some 3,767 vascular plant species, including 1,793 species (48%) endemic to China and 205 species endemic to the site itself. Amongst the rich fauna, 92 mammal and 399 species of birds have been recorded, with numerous rare and endangered species such as golden snub-nosed monkey, clouded leopard, Asiatic dhole, black bear, musk deer, Chinese goral, serow and giant salamander (the world’s largest amphibian).
Conservation Status and Prospects. According to IUCN’s Conservation Outlook Assessment (2020) the conservation status of the Hubei Shennongjia Nature Reserve is ‘good, with some concerns’. The IUCN report anticipates extension of the site to include Wulipo Nature Reserve in neighbouring Chongqing Province, which will include lower altitude forests which serve as important winter refuge habitat for many birds and mammals. It notes that tourism to the site is growing rapidly with corresponding pressure for supporting infrastructure, and highlights the need for management intervention in the reserve’s buffer zones to support sustainable livelihoods for local communities while limiting potentially damaging developments such as expansion of tea cultivation in these areas. The IUCN report also mentions the threat of infrastructure development, with specific reference to a national road that bisects the site. Hunting, poaching, unauthorized logging and firewood collection are thought to be taking place, but the extent of the threat they pose is unknown.
Links:
Google Earth
Official UNESCO Site Details
IUCN Conservation Outlook
UNEP-WCMC Site Description
Birdlife IBA
Slideshow description
The slideshow ‘tells the story’ of Hubei Shennongjia Nature Reserve with a portfolio of photos that illustrate its landscape features, cultural attributes and some of the typical plants and animals. It starts with photos of the impressive Yan Emperor Shennong Altar set against the forest-clad mountains of the reserve, and continues with images of some of the site’s iconic karst rock features, caves and waterfalls as well as general landscape views within the forest and high sub-alpine meadows. Throughout the slideshow, some of the typical plants and animals are shown, including some of the iconic rare and endangered species such as (in order of appearance): musk deer, clouded leopard, Reeve’s pheasant, golden snub-nosed monkey, Chinese goral, Asian black bear, Chinese giant salamander and Chinese serow.
The following Flickr photographers and other sources are acknowledged with thanks for their contributions to this slideshow (as credited in the watermark of each photo): Fu Xiang, Dhugal Fletcher, Samuel Yuan, Michael Olea, dbergkamp10, Kevin, Patricia Garrido, eMammal, Renzo Dionigi, Brian Shreeve, Rebecca Kepich, Jay, Aaron Qazzimir, Mandenno Photography, Richard Jackson and Tim Melling. Note that some of the close-up photos of animals are from other locations (including animals in captivity), and these are included for illustrative purposes, as representatives of the species found in the area. In some cases, these may belong to different sub-species and/or vary slightly in appearance from individuals from Hubei Shennongjia.
Factfile
Website Category:
Temperate & Boreal Forests
Area: 733 km2
Inscribed: 2016
UNESCO Criteria:
- Ecological processes (ix);
- Natural habitat for biodiversity (x);